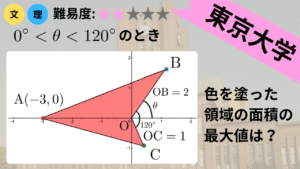
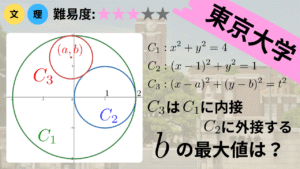
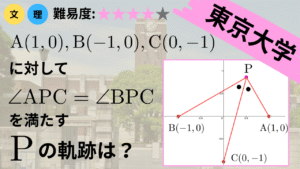
今回はこちらの問題を解いていきます.
\(xy\)平面上に2点\(\mathrm{A}\), \(\mathrm{B}\)があり, \(\mathrm{A}\)の座標は\((2,1)\)であり, \(\mathrm{B}\)は第1象限にある. \(\mathrm{O}\)を原点とし, \(\displaystyle |\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OB}}|=\sqrt{10}\), \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OA}}\perp\overrightarrow{\mathrm{AB}}\)が成り立っている. このとき, 以下の問いに答えよ.
(1) 点\(\mathrm{B}\)の座標を求めよ.
(2) \(s\), \(t\)を正の実数とし, \(\displaystyle \overrightarrow{\mathrm{OC}}=s\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OA}}+t \overrightarrow{\mathrm{OB}} \)で定まる点\(\mathrm{C}\)に対して, 三角形\(\mathrm{OAC}\)の面積と三角形\(\mathrm{OBC}\)の面積が等しく, \(\displaystyle |\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OC}}|=4\)であるとき, \(s\), \(t\)の値を求めよ.
(2025 九州大学 文系 [2])
こちらはベクトルの基本問題です.
それでは解いていきましょう.
(1) \(B\)の座標を\((a, b)\)とおくと, \(B\)は第1象限にあるから, \(a\), \(b\)は共に正である. \(\displaystyle |\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OB}}|=\sqrt{10}\)より,
$$
|\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OB}}|^2=a^2+b^2=10\,\,\,・・・①
$$が成り立つ必要がある. また, \(\displaystyle \overrightarrow{\mathrm{AB}}=(a-2, b-1)\)であるから,
$$
\begin{align}
\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OA}}\perp\overrightarrow{\mathrm{AB}} & \iff \overrightarrow{\mathrm{OA}}\cdot\overrightarrow{\mathrm{AB}}=0\\[1.5ex]
& \iff (2, 1)\cdot (a-2, b-1)=0 \\[1.5ex]
& \iff 2(a-2)+(b-1)=0\\[1.5ex]
& \iff b=-2a+5\,\,\,・・・②
\end{align}
$$となる. ②を①に代入して,
$$
\begin{align}
&a^2+(-2a+5)^2=10 \\[1.5ex]
&\iff 5a^2-20a+15=0\\[1.5ex]
&\iff a^2-4a+3=0\\[1.5ex]
&\iff (a-3)(a-1)=0\\[1.5ex]
&\iff a=1\,\,\, または\,\,\, a=3
\end{align}
$$がわかる. \(a=3\)のとき, \(b=-2\cdot a+5=-1\)となるが, これは\(b>0\) に反するので不適である. よって, \(a=1\), \(b=-2\cdot a+5=3\)が解となり, \(\mathrm{B}\)の座標は\((1, 3)\)である.
(2) \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OC}}\)を\(s\), \(t\)を用いて成分表示すると,
$$
\begin{align}
\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OC}}&=s\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OA}}+t\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OB}}\\[1.5ex]
&=s(2, 1)+t(1, 3)\\[1.5ex]
&=(2s+t, s+3t)
\end{align}
$$となる.
これから三角形\(\mathrm{OAC}\)の面積は,
$$
\triangle{\mathrm{OAC}}=\frac{1}{2}\left|2(s+3t)-(2s+t)\right|=\frac{1}{2}|5t|=\frac{5t}{2}
$$であり, 三角形\(\mathrm{OBC}\)の面積は,
$$
\triangle{\mathrm{OBC}}=\frac{1}{2}\left|(s+3t)-3(2s+t)\right|=\frac{1}{2}|-5s|=\frac{5s}{2}
$$となる(絶対値を外す際に, \(s, t>0\)を用いた). この2つの面積が等しいから,
$$
\frac{5t}{2}=\frac{5s}{2}\iff s=t
$$ となる.
これから, \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OC}}=(3s, 4s)\)と表せ, \(\displaystyle |\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OC}}|=4\)より,
$$
|\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OC}}|=\sqrt{(3s)^2+(4s)^2}=5s=4
$$であるから, \(\displaystyle s=\frac{4}{5}\)となり, \(s=t\)より, \(\displaystyle s=t=\frac{4}{5}\)である.
youtubeでも解説しています.